How to Run an Effective JHSC
Onsite Safety Management Inc.
WHAT IS A JHSC?
JHSC stands for Joint Health and Safety Committee
WHAT DOES A JHSC DO?
The purpose of the JHSC is to identify hazards and make recommendations to the employer to control the hazards.
The JHSC is an integral part of the company’s Internal Responsibility System (IRS).
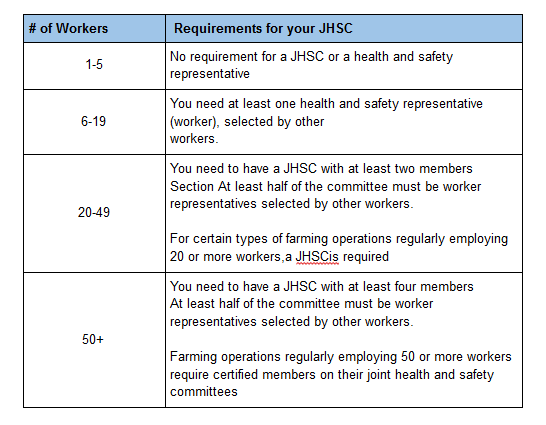
WHAT ARE THE REQUIREMENTS IN ALBERTA FOR MY JHSC?
Requirements are mostly based on the size of your company
Keep in mind that if your workplace uses a designated substance a JHSC is required.
For the legal descriptions of these requirements and further information see the JHSC Alberta Handbook.
WHAT ARE THE RESPONSIBILTIES OF JHSC MEMBERS?
The JHSC ensures that there is common ground for working on health and safety issues first and foremost.
Duties of members include:
- Meeting at least once every three months
- Maintaining and keeping minutes of meetings
- Post the names and work locations of committee
- Inspect the workplace at least once a month according to a schedule
- (or where it is not practical, inspect a portion of the workplace at least once a month so entire workplace is inspected yearly.)
- Make written recommendations for improvement in health and safety of workers to the employer
- Identify workplace hazards
- Being present at the beginning of workplace testing
- Be present at investigations of work refusals and have the right to investigate critical injuries or fatalities
- Participate in information gathering
- Accompany a Ministry of Labour inspector during a physical inspection of the workplace
EMPLOYER RESPONSIBILITIES
The responsibilities of the employer under the Occupational Health and Safety Act include:
- Establish and maintain a joint health and safety committee
- Provide paid time for JHSC members to carry out their duties
- Ensure proportional representation of workers and the employer
- Ensure that the legally required number of certified members is met
- Respond to recommendations from the JHSC within twenty-one days
- Provide any documentation or information concerning health and safety issues in the company
Recommendations for employers to support of the JHSC:
- Recognizing and rewarding the JHSC’s work
- Taking responsibility themselves for the health and safety of their workers
- Guiding the development of specific health and safety objectives, when requested
- Having senior managers promote health and safety issues
- Integrating health and safety into day-to-day activities at all levels
SETTING UP A JHSC IN 3 STEPS
1 - Identify the Need
First, the employer identifies that there is a need for a JHSC and consults provincial health and safety guidelines to determine the
minimum number of members required and what proportion of representation is necessary.
Questions for the employer:
- Will everyone be represented on the committee?
- Have I allowed for representation from part-time workers, multiple shifts, contract workers and senior workers?
When a union is established, their members of the committee are selected by them. This is sometimes part of the company’s collective bargaining agreement (CBA). Check the CBA to see how the process works.
2 - Select Management Members
The employer will appoint the management members.
3 - Select Worker Members
Workers select people to be on the committee. Once nominations are received, voting takes place. All workers have the right to vote.
HOW TO FIND PEOPLE FOR A SUCCESSFUL JHSC
In the event that there are no volunteers for the JHSC, there are several strategies that can be used to encourage people to come forward. Some of these are:
Providing basic information about the JHSC so workers understand the role
Reinforce the fact that workers will be paid for time spent fulfilling duties on the JHSC
Reassure them that they will receive basic training on the JHSC and its functions
Point out that being a part of the JHSC is a valuable addition to their resume
DIFFERENT MEMBER ROLES ON THE JHSC
Co-chairs - ensure meetings are held, run with fullfilled and recommendations are made to the employer. Co-chairs alternate chairing the meetings.
The process for selecting the co-chairs would be decided at the first meeting:
a) By nomination and election
b) Picked if only one person nominated
The management co-chair is selected by the management representatives on the committee; the worker
co-chair is selected by the worker representatives on the committee.
Secretary - Takes minutes.
The secretary position can be filled in three ways:
- It can be filled by a JHSC member – one member always takes the minutes
- By rotating the secretary function among the JHSC members with the exception of the co-chairs
- A person not on the committee may be chosen to record the minutes
Certified Members - selected or designated by the management members and worker members respectively. There must be at least one management certified member and one worker certified member.
If there is a trade union at the workplace the union would be involved in determining who among the worker members on the committee is to be the certified member.
General Members - contribute to decision making, being part of sub-committees to work on special projects; can participate in inspections.
Creating a Vision for the Committee
It is important to set a direction for the JHSC to help it meet its goals. The following questions can help:
- Does the JHSC align itself with the goals and objectives of the company?
- What are the company’s goals and objectives?
- What roles will the JHSC play in contributing to company goals and objectives?
- What are the priorities of the business?
- What are the priorities for the JHSC?
The benefit to knowing where the company is going and how it intends to get there ensures that the JHSC’s recommendations will be written in consideration of these goals and objectives and therefore be sustainable.
MAKING EFFECTIVE RECOMMENDATIONS
Effective recommendations are clear and specific.
Effective Recommendations:
- Promote continuous improvement of performance
- Are based on factual, detailed, expert data
- Focus on organizational strengths
- Incorporate best practices
- Address opportunities and threats
- Reduce or eliminate health and safety risks and unsafe practices
- Eliminate factors that contribute to uncontrolled hazards
- Stop practices that violate legal requirements
- Remove barriers to safe work practices
- Promote compliance with legislative requirements
- Improve cooperation and understanding
Track the recommendations at JHSC meetings.
They should appear on the agenda until they are resolved or there is a response from management.
If there is no response within 21 days, the JHSC:
- should follow-up with management
- Make sure to include the facts and evidence that support the recommendation
HOW A EMPLOYER SHOULD RESPOND TO A JHSC RECOMMENDATION
The response to the recommendation must be submitted to the JHSC in writing.
There are three ways the employer can respond:
Accept the recommendation and take action
Decide to use an alternative solution that meets the need and take action
Decline the recommendation and take no action
When the employer accepts the recommendation as proposed, a response should include:
The proposed recommendation
What is accepted
The goal
A time frame
The management person assigned to complete key activities
If the employer responds negatively to the recommendation or with a revised proposed solution, the written response must clearly explain the decision to the JHSC.